Clinical and Economic Impact of Sickle Cell Disease
Gene therapies have the potential to revolutionize medicine and improve the lives of individuals living with sickle cell disease (SCD). Additional considerations such as high costs for these therapies and questions regarding insurance coverage remain major challenges to patient accessibility and further development.
The Clinical and Economic Impact Analysis (CEIA) Consortium
The Cure Sickle Cell Initiative (CureSCi) formed the Clinical and Economic Impact Analysis (CEIA) Consortium in 2019 to help identify and evaluate the cost effectiveness of gene therapies for SCD. The Consortium was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) through awards to the University of Washington (UW) and the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center (FH). The investigators from both institutions received feedback and guidance from an expert panel consisting of individuals living with sickle cell disease, advocates, clinicians with expertise in pediatric and adult sickle cell disease care and bone marrow transplant, as well as bioethicists, health economists, database analysts, and members of the payer community.
CEIA Mission
The CEIA’s mission was to develop simulation models that can be used to demonstrate the potential national impact of specific curative therapies for SCD, and the distribution of that impact on payers, employers, and families over the lifetime of the patients.
Models for Economic Analysis of SCD
Two independently developed simulation models were designed to assess lifetime outcomes with and without gene therapy for people living with SCD. The FH's Sickle Cell Disease Outcomes Research and Economics Model (FH-HISCORE) and the
UW Model for Economic Analysis of Sickle Cell Cure (UW-MEASURE) were published in the
Annals of Internal Medicine
in January 2024.
The UW-MEASURE microsimulation model web portal, which uses the R-Shiny platform, allows users to examine and adjust values that help to estimate healthcare and societal outcomes of SCD gene therapies.
“Both the UW and Fred Hutch models suggest that gene therapies can be life-altering for patients with sickle cell disease. We show prolonged, substantial reductions in pain crises events and reduced morbidity over time, greatly improving patients' prospects for long-term employment, decreasing or possibly eliminating caregiver burden, and substantially improving recipients' life expectancy and quality of life compared to current standards of care. The long-term durability of therapy is an important unknown that will impact cost-effectiveness. Future work comparing the clinical and economic effects of gene therapy versus stem cell transplantation will assist in guiding patients to the most appropriate and cost-effective therapy.”
SCOTT RAMSEY, MD, PHD
Principal Investigator


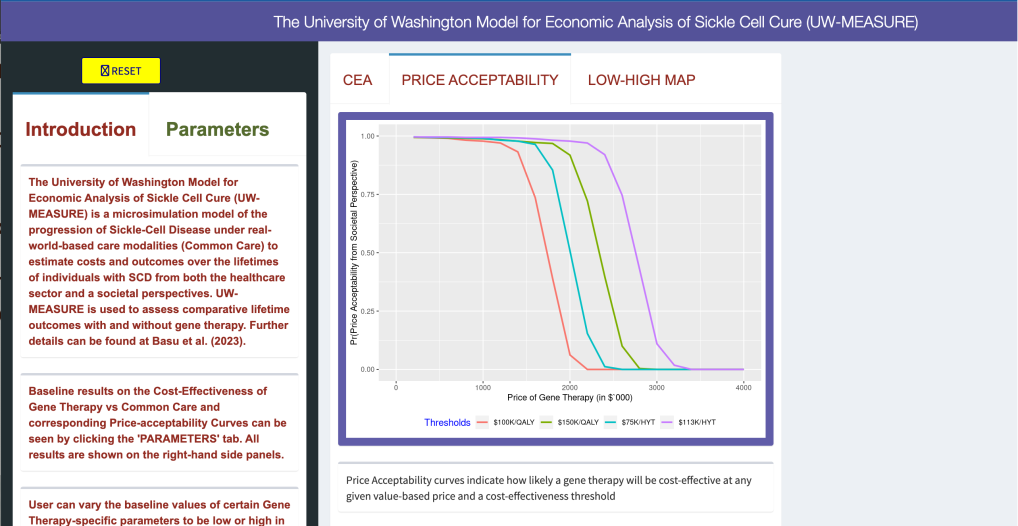
 “Gene Therapy Versus Common Care for Eligible Individuals with Sickle Cell Disease in the United States: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis,” Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Gene Therapy Versus Common Care for Eligible Individuals with Sickle Cell Disease in the United States: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis,” Annals of Internal Medicine.